
The ratio can provide insights into the financial health of a company and help evaluate the effectiveness of investments as well as pricing strategies. The ratio can also offer clues on how to better manage working capital and reduce the company’s operating costs. Furthermore, the working capital turnover ratio can also be used to assess the effectiveness of a company’s inventory management.
Times interest earned ratio: Formula, definition, and analysis
Another potential cause of cash flow problems is delays in collecting payments from customers. By analysing the working capital turnover ratio, investors and analysts can gain a better understanding of a company’s liquidity and operational efficiency. Working capital turnover ratio is an essential metric managers can use for financial decision-making.
Rare American Coins That Are Worth a Lot of Money
- One of the most effective ways of using the working capital turnover ratio to measure business efficiency is by comparing it with the industry average.
- ” I have a feeling that improving your working capital turnover ratio would be exactly what he means.
- If a business takes on additional debt after an increase in interest rates, the total annual interest expense will be higher.
- This indicates the company lacks the short-term resources to pay its debts and must find ways to meet its short-term obligations.
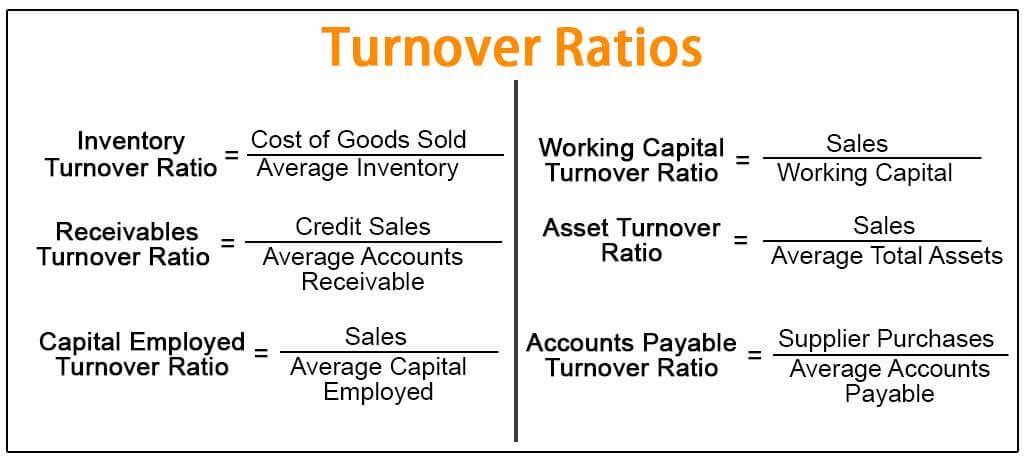
One way to measure this metric is to understand a business’s asset turnover ratio. Learn more about what exactly an asset turnover ratio is and how it’s calculated. For example, if a company has $100,000 in current assets and $30,000 in current liabilities, it has $70,000 of working capital. This means the company has $70,000 at its disposal in the short term if it needs to raise money for any reason. This ratio measures the number of times a company’s working capital is used to generate revenue over a given period.
Sending you timely financial stories that you can bank on.
Both figures can be found in public companies’ publicly disclosed financial statements, though this information may not be readily available for private companies. A low working capital turnover ratio may also indicate that a company is not generating enough cash from its operations to sustain its growth. In this case, the company may need to consider ways to increase its operating cash flow, such as reducing expenses or improving its sales processes. Overall, the working capital turnover ratio is a useful tool for assessing a company’s efficiency in using its working capital to generate revenue. By using this ratio, companies can identify areas where they may be able to improve their operations and make better investment decisions. Working capital turnover is a way to measure how your company uses available capital to fund sales and growth.
Using Industry Benchmarks to Compare Your Business’s Working Capital Turnover Ratio
It’s also meant to shed light on whether your operations are making progress every year. If your company has a low ratio, this could be a sign that you’re spending on too many accounts receivable and inventory to support your sales. As such, you could end up with too much bad debt, or a load of obsolete inventory.
Working capital refers to the money your business has available to spend on essential payments, operations, etc. after all bills and debt installments have been paid. Working capital turnover measures the relationship between the funds used to finance a company’s operations and the revenues a company generates to continue operations and turn a profit. A higher times interest earned ratio means that the business is generating more earnings, or that the business has reduced total interest expense — or both. Companies may use earnings to pay dividends to shareholders, or retain earnings to fund business operations. Ideally, a business should generate enough earnings to pay for interest expenses and to fund other needs. Reducing net debt and increasing EBITDA improves a company’s financial health.
To determine a financially healthy ratio for your industry, research industry publications and public financial statements. Keep in mind that earnings must be collected in cash to make interest payments. While the TIE ratio does not account for cash, managers must collect sufficient cash to make interest payments. This article explores the times interest earned (TIE) ratio, provides several examples of its application, and explains how your business can improve the ratio’s value over time. To stay on top of profitability, they will assess ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, incentivize employees and optimize operations to maximize the bottom line. Therefore, as of March 2024, Microsoft’s working capital metric was approximately $28.5 billion.
If the TIE ratio decreases, the company may be generating lower earnings or issuing more debt (or both). Depending on the industry, a high or low ratio may mean different things. Still, it’s important to look at the types of assets and liabilities and the company’s industry and business stage to get a more complete picture of its finances.
A higher ratio indicates that a company is generating more sales with its available working capital, while a lower ratio suggests that a company may not be using its working capital effectively. Working capital is to a business as wind is to a sailboat — sure, you might be able to drift along without it, laboriously paddling to avoid the rocks, but you really need it to make good progress. A downward trend in the working capital turnover ratio can indicate for example that accounts receivable (current assets) are increasing as sales increase. Eventually this will result in the business being unable to fund its working capital requirement and a cash flow shortage. Working capital turnover ratio (WCTR) is a crucial financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in utilizing its working capital to generate sales.
By monitoring the ratio over a period of time, businesses can identify if their working capital management is improving or deteriorating. This information can help businesses make informed decisions about their working capital management strategies and take corrective actions if necessary. Even a profitable business can face bankruptcy if it lacks the cash to pay its bills. For example, if a company has $1 million in cash from retained earnings and invests it all at once, it might not have enough current assets to cover its current liabilities. To calculate working capital, subtract a company’s current liabilities from its current assets.
He specializes in transitioning traditional bookkeeping into an efficient online platform that makes preparing financial statements and filing tax returns a breeze. In his freetime, how to professionally ask for payment from clients template you’ll find Grant hiking and sailing in beautiful British Columbia. Interpretation of this ratio should be done when inter-firm or inter-period comparison is being done.
